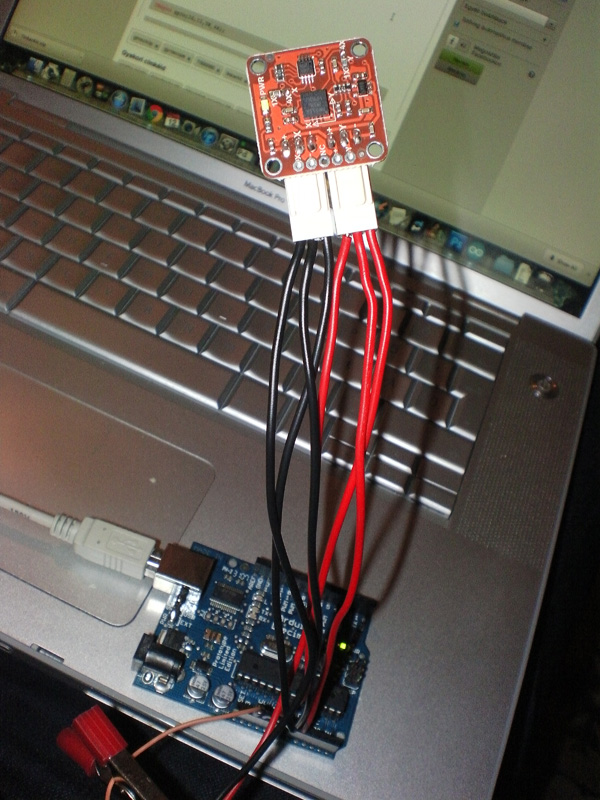
A digitális giroszkóp egy 3d-s gyorsulásérzékelő chip. A Föld mágneses pólusait (Észak, Dél) érzékeli és abból számolja az elmozdulást. Ebben a példában a dölés szöget és az mozdulat sebességét tudjuk kiolvasni serial monitoron.
A tinkerkit library-t is telepíteni kel hozzá, innen:
http://tinkerkit.com/en/Tutorials/Home
Hivatkozások:
TKGyro gyro(I0,I1,TK_4X);gyro.getXAxis();
//x tengely értéke 0-1023gyro.getYAxis();
//y tengely értéke 0-1023gyro.getXAxisRate();
//x tengely fizikai helyzete: -6000°/s-tól 6000°/s-iggyro.getYAxisRate();
//y tengely fizikai helyzete: -6000°/s-tól 6000°/s-ig
TinkerKit Gyroscope 2 Axis sensitivity 1X
Bekötése:
x tengely A0
y tengely A1
+ pinek 5V-ba mindkettő
- pinek Gnd-be mindkettő
Arduino kód a hivatalos Manual-ból:
/* TinkerKit! Gyroscope [T000060-64]
*
* This sketch shows how to read this 2-axis gyroscope,
* turning in a given angular velocity and then converting it
* in the simplest way in an angular position (/inclination).
*
* Connect: the X-axis to the Analog Input Pin 0 (I0)
* the Y-axis to the Analog Input Pin 1 (I1)
* Optional: connect a servo to Analog Output Pin 9 (O2)
*
* created by Federico Vanzati / f.vanzati@arduino.cc
* in September 2011
*
* inspired from www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/Gyro
* by eric barch / ericbarch.com
*/
#include <Servo.h>
// Pin used in this example
#define SERVO 9
#define X_GYRO 0
#define Y_GYRO 1
#define ADCresolution 4.89f // = 5000mV/1023counts: Arduino analog pins resolution expressed in mV/count
#define Sensitivity 0.67f // [mV/dps] sensitivity of the sensor, took from datasheet (4x output mode)
// Conversion coefficient, we do here because is a constant! so we'll not do the calculation every loop
#define K ADCresolution/Sensitivity // the constant!
#define nrSamples 6 // Number of samples that we take for each measure
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// a maximum of eight servo objects can be created
// Timing variables
unsigned long time, sampleTime = 12;
unsigned long printTime = 0, serialRefresh_time = 500;
float deltaT = (float)sampleTime*nrSamples/1000;
//Gyroscope variables
int roll_zeroVoltage, pitch_zeroVoltage;
int roll_rawADC[nrSamples], pitch_rawADC[nrSamples]; // store 3 values...just to avverage
float roll_rate, pitch_rate; //
float roll_angle = 0, pitch_angle = 0;
int c=0; // just a counter to count the samples
int pos; // variable to store the servo position
void setup()
{
delay(1000);
myservo.attach(SERVO); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
myservo.write(pos);
Serial.begin(57600);
Serial.print("TinkerKit! Gyroscope [T000062] Test Example\n\n");
int correctionY=0, correctionX=0;
for (int i=0; i<50; i++)
{
correctionY += analogRead(Y_GYRO);
correctionX += analogRead(X_GYRO);
delay(20);
}
roll_zeroVoltage = correctionY/50;
pitch_zeroVoltage = correctionX/50;
Serial.print(roll_zeroVoltage);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(pitch_zeroVoltage);
time = millis();
}
void loop()
{
// Every 40ms take a sample from gyro
if(millis() - time > sampleTime)
{
time = millis();
roll_rawADC[c] = analogRead(Y_GYRO);
pitch_rawADC[c] = analogRead(X_GYRO);
c++;
}
if(c==nrSamples) // Well, we have 3 samples
{
// Transform the raw data into an angular velocity
roll_rate = (filterGyro(roll_rawADC) - roll_zeroVoltage) * K;
pitch_rate = (filterGyro(pitch_rawADC) - pitch_zeroVoltage)*K;
// Integrate the angular veloity to obtain angular position (or inclination)
// Using the trapeziod method for numerical integration
// sampleTime*nrSamples
// The variable that take mind of the integration time is deltaT = --------------------
// 1000
// - we multiply for nrSamples because
// - divide for 1000 because angular velocity is expessed in seconds,
// but sampleTime is expressed in milliseconds
roll_angle += roll_rate*deltaT/2;
pitch_angle += pitch_rate*deltaT/2;
//Keep our angle between 0-359 degrees
if (roll_angle < 0)
roll_angle += 360;
else if (roll_angle > 359)
roll_angle -= 360;
if (pitch_angle < 0)
pitch_angle += 360;
else if (pitch_angle > 359)
pitch_angle -= 360;
// Now we control the servo: home position is setted in the center at 90 degrees
if(roll_angle >= 0 && roll_angle <= 90) // counterclockwise rotation of the gyro...
pos = 90 + (int)roll_angle; // ...produces rotation from 90 to 180 deg on servo
if(roll_angle >= 270) // clockwike rotation of the gyro...
pos = (int)roll_angle - 270; // ...produces rotation from 90 to 0 deg on servo
myservo.write(pos); // send the position to servo
if(millis() - printTime > serialRefresh_time)
{
printTime = millis();
Serial.print("Roll speed: "); Serial.print((int)roll_rate);
Serial.print("\t Angle: "); Serial.print((int)roll_angle);
Serial.print("\t Pitch speed: ");Serial.print((int)pitch_rate);
Serial.print("\t Angle: ");Serial.println((int)pitch_angle);
Serial.print("Servo: "); Serial.println(pos);
}
c=0; // reset the counter
}
}
int filterGyro(int buffer[])
{
int mean=0;
for(byte i=0; i<nrSamples; i++)
mean += buffer[i];
mean /= nrSamples;
return mean;
}
Egy példa, grafikus interfész processingben, ami a giró adatait mutatja: http://scuola.arduino.cc/en/content/realizziamo-uninterfaccia-grafica-modulo-giroscopio-tinkerkit
forrás
http://www.tinkerkit.com/bp/reference/, http://tinkerkit.com/en/Tutorials/Home, http://sensorwiki.org/doku.php/sensors/gyroscope